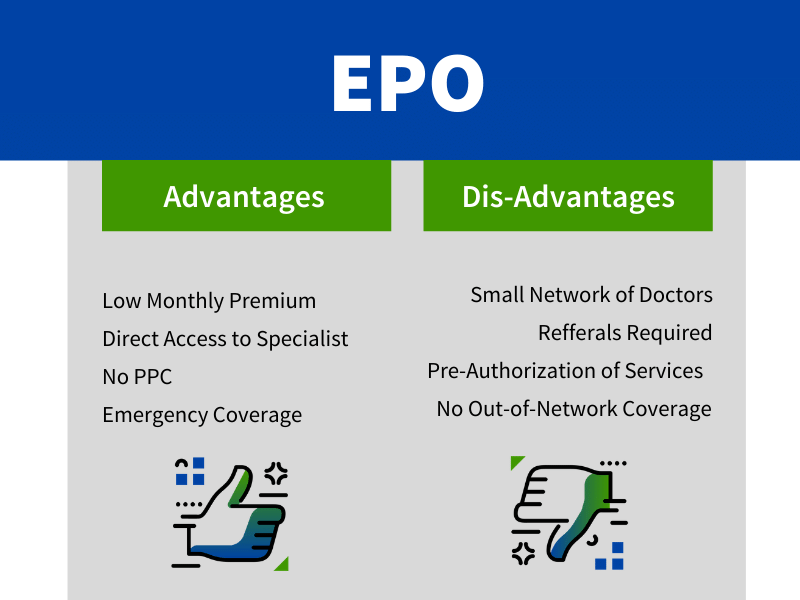
EPO insurance sets the stage for this informative guide, offering readers a comprehensive overview of this unique health plan. EPO insurance, also known as Exclusive Provider Organization insurance, stands out from traditional health insurance plans like HMOs and PPOs by offering a blend of cost savings and provider access. Understanding EPO insurance requires delving into its key features, advantages, and disadvantages, as well as comparing it to other health plan options.
This guide will explore the intricacies of EPO insurance, providing insights into its network structure, cost-sharing mechanisms, and potential benefits. It will also examine the considerations involved in choosing an EPO plan, including factors such as individual needs, budget, and health status. By shedding light on the nuances of EPO insurance, this guide aims to empower individuals with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about their healthcare coverage.
EPO Insurance and Healthcare Reform
EPO insurance plans have been significantly impacted by healthcare reform legislation, particularly the Affordable Care Act (ACA). The ACA’s aim to expand health insurance coverage and regulate the healthcare market has led to changes in EPO plan design, benefits, and eligibility requirements.
Impact of Healthcare Reform on EPO Insurance Plans
The ACA has had a profound impact on EPO insurance plans. Key changes include:
- Essential Health Benefits: The ACA mandates that all health insurance plans, including EPOs, must cover essential health benefits, such as preventive care, hospitalization, and prescription drugs. This has broadened the scope of coverage offered by EPO plans, potentially increasing premiums.
- Premium Tax Credits: The ACA provides premium tax credits to individuals and families with moderate incomes to help them afford health insurance. These credits can be applied to EPO plans, making them more accessible to a wider range of individuals.
- Individual Mandate: The ACA’s individual mandate requires most Americans to have health insurance or face a penalty. This has driven many individuals to enroll in EPO plans, as they often offer lower premiums compared to other types of health insurance.
- Medical Loss Ratio (MLR): The ACA requires health insurers to spend a certain percentage of their premium revenue on medical care, known as the medical loss ratio. This has influenced the design of EPO plans, as insurers need to ensure they meet the MLR requirements.
Future Trends and Developments in EPO Insurance
The future of EPO insurance is likely to be shaped by ongoing healthcare reform efforts and evolving consumer preferences. Potential trends include:
- Increased Transparency: Consumers are increasingly demanding greater transparency in healthcare costs and plan benefits. EPO plans may need to adapt to this trend by providing more detailed information about pricing and coverage.
- Focus on Value-Based Care: The healthcare industry is shifting towards value-based care, which emphasizes quality of care over quantity. EPO plans may incorporate value-based care principles by offering incentives for preventive care and managing chronic conditions effectively.
- Integration with Technology: The use of technology in healthcare is rapidly increasing. EPO plans may integrate with telehealth platforms, mobile health apps, and other digital tools to enhance convenience and improve patient engagement.
Role of EPO Insurance in the Broader Healthcare Landscape
EPO insurance plans play a significant role in the broader healthcare landscape. They provide affordable health insurance coverage to individuals and families, often with lower premiums than other types of plans. EPOs can also contribute to cost containment by promoting the use of in-network providers and encouraging preventive care. However, it’s important to note that EPO plans may limit access to out-of-network providers, which could be a concern for individuals who require specialized care or live in areas with limited provider networks.
EPO Insurance and Employer-Sponsored Plans
EPO insurance plans are often offered by employers as part of their employee benefits package. Employers play a crucial role in making these plans accessible to their workforce.
EPO plans can be a valuable addition to an employer’s benefits package, offering both advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of EPO Plans for Employers
EPO plans offer several benefits for employers, making them an attractive option for businesses of all sizes.
EPO insurance, or Exclusive Provider Organization, offers a balance between HMO and PPO plans. You get a network of providers to choose from, but you’ll pay more for out-of-network care. If you’re looking for a cost-effective plan, you might want to explore options from cheap insurance companies , as they often have competitive EPO plans.
Remember to compare quotes and features to find the best EPO insurance for your needs.
- Lower Premiums: EPO plans generally have lower premiums compared to traditional PPO plans, which can result in cost savings for employers.
- Reduced Administrative Costs: EPO plans often have simpler administrative processes, reducing the administrative burden on employers and saving them money.
- Improved Employee Health: EPO plans can encourage employees to seek preventive care and manage their health proactively, leading to improved overall employee health and reduced healthcare costs in the long run.
- Increased Employee Satisfaction: EPO plans can provide employees with access to quality healthcare at an affordable price, leading to increased employee satisfaction and retention.
Disadvantages of EPO Plans for Employers
While EPO plans offer several advantages, employers should also consider potential drawbacks before implementing them.
- Limited Network: EPO plans have a limited network of providers, which can restrict employee choices and potentially lead to longer wait times for appointments.
- Out-of-Network Costs: EPO plans generally do not cover out-of-network services, which can result in significant out-of-pocket expenses for employees if they need to see a provider outside the network.
- Potential for Higher Deductibles: Some EPO plans may have higher deductibles than traditional PPO plans, which could increase the financial burden on employees.
Examples of EPO Plans in Different Industries
EPO plans are commonly used in various industries and business sectors, catering to the specific needs of different employee demographics and healthcare requirements.
- Technology Industry: Tech companies often offer EPO plans to their employees, who are typically younger and healthier, and may be more comfortable with the limited network and lower premiums.
- Education Sector: Schools and universities often offer EPO plans to their faculty and staff, providing access to affordable healthcare options while managing costs effectively.
- Manufacturing Industry: Manufacturing companies, with large workforces, often opt for EPO plans to reduce healthcare costs and provide their employees with access to essential medical services.
EPO Insurance and Individual Market
EPO plans are generally available in the individual market, but their availability may vary depending on the state and the insurance company. While EPO plans are typically associated with employer-sponsored programs, some insurance companies offer them directly to individuals.
Availability of EPO Plans in the Individual Market
EPO plans are not as common in the individual market as other types of health insurance plans, such as HMOs and PPOs. This is because EPO plans typically have a narrower network of providers, which can make it more difficult for individuals to find a doctor or hospital they are comfortable with. However, there are still a number of insurance companies that offer EPO plans in the individual market, and their availability is growing.
Challenges of Purchasing EPO Plans Independently
There are a number of challenges that individuals may face when purchasing EPO plans independently.
- Limited Network of Providers: One of the biggest challenges is finding a doctor or hospital within the plan’s network. This can be especially difficult for individuals who have specialized healthcare needs.
- Higher Premiums: EPO plans may have higher premiums than other types of health insurance plans, such as HMOs. This is because EPO plans typically have lower out-of-pocket costs, which means that the insurance company has to pay more for healthcare services.
- Limited Choice of Plans: The number of EPO plans available in the individual market may be limited, especially in certain geographic areas.
- Difficulty Navigating the Market: It can be difficult for individuals to navigate the individual health insurance market and find an EPO plan that meets their needs.
Opportunities of Purchasing EPO Plans Independently
Despite the challenges, there are also some opportunities for individuals who purchase EPO plans independently.
- Lower Out-of-Pocket Costs: EPO plans typically have lower out-of-pocket costs than other types of health insurance plans. This can be a major advantage for individuals who are concerned about the cost of healthcare.
- Potential for Lower Premiums: While EPO plans may have higher premiums in some cases, they can also have lower premiums in others. This is because insurance companies can offer lower premiums to individuals who are willing to accept a narrower network of providers.
- Growing Availability: The availability of EPO plans in the individual market is growing. This means that individuals have more options to choose from and are more likely to find a plan that meets their needs.
Resources for Individuals Seeking EPO Plans
There are a number of resources available to help individuals find EPO plans in the individual market.
- Health Insurance Marketplace: The Health Insurance Marketplace is a website where individuals can compare and enroll in health insurance plans. The Marketplace offers a variety of health insurance plans, including EPO plans.
- Insurance Brokers: Insurance brokers can help individuals find EPO plans that meet their needs. Brokers have access to a wide range of insurance companies and plans, and they can provide personalized advice.
- Insurance Company Websites: Individuals can also search for EPO plans directly on the websites of insurance companies. Many insurance companies offer online tools that allow individuals to compare plans and get quotes.
Epilogue
As you navigate the world of health insurance, understanding EPO insurance can be a valuable asset. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of EPO plans, including their key features, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for choosing the right plan. By weighing the pros and cons and understanding the nuances of EPO insurance, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your individual healthcare needs and preferences.
