What is commercial insurance? It’s a safety net for your business, safeguarding you from financial losses caused by unforeseen events. Unlike personal insurance that covers individuals, commercial insurance is tailored to protect businesses, their assets, and their operations.
Imagine a small bakery facing a fire that destroys its ovens and inventory. Commercial insurance can provide financial support to rebuild, replace equipment, and cover lost income, allowing the bakery to recover and continue serving its customers.
Types of Commercial Insurance
Commercial insurance provides protection for businesses against various risks that could lead to financial losses. It is crucial for companies to understand the different types of commercial insurance available to ensure they have adequate coverage for their specific needs.
Common Types of Commercial Insurance
This section provides a comprehensive overview of common commercial insurance types, outlining the risks covered by each and the typical industries that benefit from them.
| Insurance Type | Coverage | Typical Industries |
|---|---|---|
| General Liability Insurance | Protects against claims of bodily injury or property damage caused by the insured’s business operations or products. This includes coverage for legal defense costs and settlements. | All industries, especially those with customer interaction, product manufacturing, or potential for accidents. |
| Property Insurance | Covers physical damage to a business’s property, including buildings, equipment, inventory, and furniture, due to events like fire, theft, vandalism, and natural disasters. | All industries that own physical assets, including manufacturing, retail, hospitality, and healthcare. |
| Workers’ Compensation Insurance | Provides benefits to employees who suffer work-related injuries or illnesses, including medical expenses, lost wages, and rehabilitation costs. It also protects employers from lawsuits related to employee injuries. | All industries that employ workers, including manufacturing, construction, healthcare, and retail. |
| Commercial Auto Insurance | Covers damage to company vehicles, including trucks, vans, and cars, and liability for accidents involving company vehicles. | Transportation, delivery, logistics, construction, and sales industries that use vehicles for business operations. |
| Professional Liability Insurance (Errors & Omissions) | Protects professionals, such as lawyers, doctors, accountants, and consultants, against claims of negligence, errors, or omissions in their professional services. | Professional service industries, including law firms, accounting firms, medical practices, and consulting firms. |
| Product Liability Insurance | Covers businesses against claims arising from defective products that cause injury or damage. | Manufacturing, food and beverage, and consumer goods industries that produce and sell products. |
| Cyber Liability Insurance | Protects businesses against financial losses resulting from cyberattacks, data breaches, and other cyber-related incidents. | All industries, especially those that handle sensitive data, such as financial institutions, healthcare providers, and technology companies. |
| Business Interruption Insurance | Provides coverage for lost income and expenses when a business is forced to shut down due to an insured event, such as a fire, flood, or power outage. | All industries, especially those with high operating costs or significant revenue streams. |
| Directors and Officers (D&O) Liability Insurance | Protects directors and officers of a company against personal liability for wrongful acts or omissions related to their duties. | Publicly traded companies, non-profit organizations, and large private companies. |
| Employment Practices Liability Insurance | Covers businesses against claims related to employment practices, such as discrimination, harassment, wrongful termination, and wage and hour violations. | All industries that employ workers, especially those with large workforces or complex employment policies. |
| Crime Insurance | Provides coverage for losses caused by employee dishonesty, theft, forgery, and other criminal acts. | All industries, especially those that handle cash, valuable assets, or sensitive information. |
| Fidelity Bond | Protects businesses against financial losses caused by the dishonest acts of employees, such as embezzlement or fraud. | Financial institutions, businesses with high-value assets, and companies with employees who handle sensitive financial information. |
Benefits of Commercial Insurance
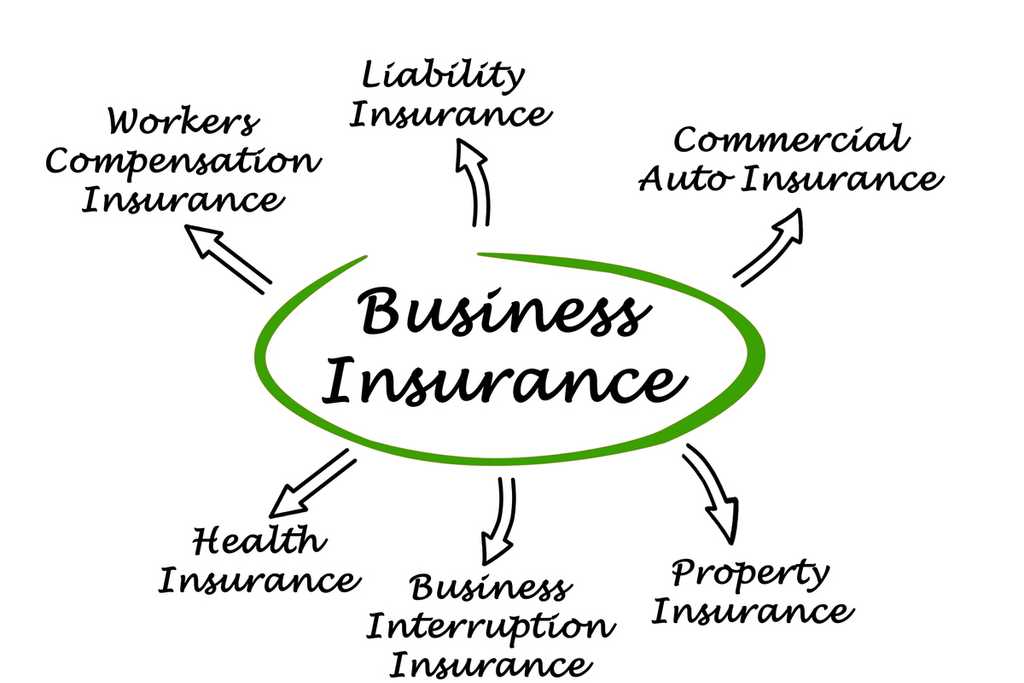
Commercial insurance offers a wide range of benefits to businesses of all sizes, providing crucial protection against financial risks and unforeseen events. These benefits can be categorized into three main areas: financial protection, liability mitigation, and business continuity.
Financial Protection
Financial protection is the most obvious benefit of commercial insurance. By transferring the risk of financial losses to the insurance company, businesses can protect their assets and ensure their financial stability.
Here are some specific examples of how commercial insurance can provide financial protection:
- Property Insurance: Covers damage or loss to business property, such as buildings, equipment, and inventory, due to fire, theft, natural disasters, or other perils. This helps businesses recover from significant financial losses and continue operating. For example, a restaurant that suffers a fire can use property insurance to rebuild the restaurant and replace lost equipment, minimizing financial disruption.
- Liability Insurance: Protects businesses from financial losses resulting from lawsuits or claims arising from injuries or property damage caused by their operations. This is crucial for businesses that interact with the public, such as retailers, restaurants, or service providers. For example, a construction company that accidentally damages a nearby property during a project can rely on liability insurance to cover the costs of repairs and legal expenses.
- Business Interruption Insurance: Covers lost income and expenses when a business is forced to shut down due to an insured event, such as a fire or natural disaster. This insurance helps businesses maintain their cash flow and cover ongoing expenses during the recovery period. For example, a manufacturing plant that experiences a flood can use business interruption insurance to pay for rent, utilities, and employee salaries while it repairs the damage and resumes production.
Liability Mitigation
Commercial insurance can also play a significant role in mitigating legal liabilities, protecting businesses from financial ruin and reputational damage.
Here are some ways commercial insurance can mitigate legal liabilities:
- General Liability Insurance: Provides broad coverage for a wide range of potential liabilities, including bodily injury, property damage, and advertising injury. This insurance protects businesses from lawsuits arising from accidents, negligence, or other incidents that occur on their premises or during their operations. For example, a coffee shop that spills hot coffee on a customer can rely on general liability insurance to cover the cost of medical expenses and legal fees.
- Product Liability Insurance: Covers businesses from financial losses arising from claims related to defective products. This is essential for manufacturers, distributors, and retailers, as it protects them from lawsuits alleging that their products caused injury or damage. For example, a toy manufacturer that produces a toy with a faulty design that causes injury to a child can rely on product liability insurance to cover the cost of medical expenses, legal fees, and product recalls.
- Professional Liability Insurance (E&O): Protects professionals, such as lawyers, doctors, accountants, and consultants, from claims of negligence or errors in their professional services. This insurance helps safeguard their reputation and financial stability by covering the cost of legal defense and settlements. For example, an accountant who makes an error in a client’s tax return can rely on professional liability insurance to cover the cost of defending against a lawsuit and any financial damages awarded to the client.
Business Continuity
Commercial insurance can also help businesses maintain their operations and recover quickly from unexpected events, ensuring their long-term success.
Here are some ways commercial insurance can contribute to business continuity:
- Business Interruption Insurance: As mentioned earlier, business interruption insurance provides financial protection during periods of business disruption, allowing businesses to continue paying expenses and maintain their cash flow. This can be crucial for businesses that rely on continuous operations, such as manufacturing plants, retail stores, or service providers. For example, a restaurant that is forced to close due to a power outage can use business interruption insurance to cover the cost of lost revenue and continue paying its employees during the closure period.
- Cyber Liability Insurance: Protects businesses from financial losses and reputational damage caused by cyberattacks, data breaches, and other cyber incidents. This insurance covers the cost of data recovery, legal expenses, and regulatory fines, helping businesses mitigate the impact of cyberattacks and ensure their continued operations. For example, a retail company that suffers a data breach can rely on cyber liability insurance to cover the cost of notifying customers, hiring cybersecurity experts, and implementing security measures to prevent future attacks.
- Workers’ Compensation Insurance: Protects businesses from financial losses related to workplace injuries and illnesses. This insurance covers medical expenses, lost wages, and disability benefits for employees who are injured or become ill while at work. It also helps businesses avoid lawsuits and protect their reputation. For example, a construction company that has an employee who is injured on the job can rely on workers’ compensation insurance to cover the employee’s medical expenses and lost wages.
Key Components of a Commercial Insurance Policy
A commercial insurance policy is a legally binding contract between an insurance company and a business owner. It Artikels the terms and conditions of the insurance coverage, including the risks covered, the premium to be paid, and the limits of liability. Understanding the key components of a commercial insurance policy is crucial for business owners to make informed decisions about their insurance needs and ensure they have adequate protection.
Policy Components
Understanding the components of a commercial insurance policy is essential for businesses to navigate their insurance needs effectively. These components work together to define the scope of coverage, financial obligations, and procedures for claims.
- Declaration Page: The declaration page is the first page of the policy and summarizes the key details of the policy, including the insured’s name, policy number, coverage periods, and the premium amount.
- Insuring Agreement: This section Artikels the specific risks covered by the policy. It defines the insurer’s commitment to provide financial protection against covered losses.
- Exclusions: This section details the risks, events, or situations that are not covered by the policy. It’s important to carefully review these exclusions to understand the limitations of your coverage.
- Conditions: This section Artikels the responsibilities of both the insured and the insurer. It includes requirements for reporting claims, providing documentation, and cooperating with investigations.
- Definitions: This section clarifies the meaning of key terms used throughout the policy. Understanding these definitions is crucial for interpreting the policy’s coverage and obligations.
Premiums, Deductibles, and Coverage Limits
Premiums, deductibles, and coverage limits are key financial components that determine the cost of insurance and the extent of coverage.
- Premiums: Premiums are the regular payments made by the insured to the insurer for the insurance coverage. The premium amount is calculated based on various factors, including the type of coverage, the risk profile of the insured, and the coverage limits.
- Deductibles: Deductibles are the amount of money the insured is responsible for paying out-of-pocket before the insurer starts covering the claim. A higher deductible usually results in a lower premium.
- Coverage Limits: Coverage limits represent the maximum amount the insurer will pay for a covered loss. The coverage limits can be set for specific events or for the policy as a whole.
Policy Components Table
The following table illustrates the common components of a commercial insurance policy:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Declaration Page | Summarizes key policy details, including insured’s name, policy number, coverage periods, and premium amount. |
| Insuring Agreement | Artikels the specific risks covered by the policy, defining the insurer’s commitment to provide financial protection. |
| Exclusions | Details the risks, events, or situations not covered by the policy, outlining limitations of coverage. |
| Conditions | Specifies responsibilities of both the insured and insurer, including reporting claims, providing documentation, and cooperating with investigations. |
| Definitions | Clarifies the meaning of key terms used throughout the policy, aiding in interpreting coverage and obligations. |
Factors Influencing Commercial Insurance Costs
Commercial insurance premiums are not fixed and vary significantly depending on several factors. These factors are crucial for insurers to assess the risk associated with each business and determine the appropriate premium.
Industry
The industry in which a business operates is a significant factor influencing its insurance costs. Different industries have varying levels of risk. For example, construction companies face higher risks than office-based businesses due to the nature of their work. Insurers use industry classifications to group businesses with similar risks and charge premiums accordingly.
Business Size
The size of a business also plays a role in determining insurance costs. Larger businesses typically have more complex operations and higher potential losses. As a result, they may face higher insurance premiums.
Risk Factors, What is commercial insurance
Several factors contribute to the risk associated with a business, impacting its insurance costs. These factors include:
- Loss History: Businesses with a history of claims or accidents may face higher premiums. Insurers consider past claims data to assess the likelihood of future losses.
- Safety Measures: Businesses with robust safety measures, such as fire suppression systems or comprehensive safety training programs, may qualify for lower premiums. Insurers reward businesses that actively manage risks.
- Location: The location of a business can influence insurance costs. Businesses in areas with high crime rates or natural disaster risks may face higher premiums.
- Business Operations: The nature of a business’s operations can also impact its insurance costs. For example, businesses that handle hazardous materials or operate in high-risk environments may face higher premiums.
Insurance Provider
Insurance providers have different underwriting practices and risk assessments. They may offer varying premiums for the same type of coverage. Comparing quotes from multiple providers is essential to secure the most competitive rate.
Importance of Risk Management
Risk management is a crucial aspect of running a successful business. It involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks that could negatively impact your operations, finances, and reputation. By proactively addressing these risks, you can protect your business from unforeseen challenges and ensure its long-term sustainability.
Role of Risk Management in Commercial Insurance
Effective risk management plays a significant role in commercial insurance. It helps businesses secure more favorable insurance premiums, minimize potential losses, and maintain a positive relationship with their insurance providers. Insurance companies often reward businesses that demonstrate a strong commitment to risk management with lower premiums and more comprehensive coverage options.
Commercial Insurance for Specific Industries
Commercial insurance policies are not one-size-fits-all. Instead, they are tailored to meet the unique needs of different industries. This ensures that businesses have the coverage they need to protect themselves from the specific risks they face.
Tailored Policies for Various Industries
Commercial insurance policies are designed to meet the specific needs of various industries. Here are some examples:
- Healthcare: Hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare providers face a wide range of risks, including medical malpractice, patient injuries, and data breaches. Their insurance policies typically include coverage for these specific risks.
- Construction: Construction companies face risks such as worker injuries, property damage, and delays. Their insurance policies typically include coverage for these risks, as well as liability for defective work.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturers face risks such as product liability, environmental damage, and worker injuries. Their insurance policies typically include coverage for these risks, as well as business interruption insurance.
- Technology: Technology companies face risks such as cyberattacks, data breaches, and intellectual property theft. Their insurance policies typically include coverage for these risks, as well as liability for product defects.
Unique Risks Faced by Specific Sectors
Each industry faces unique risks that require specific coverage. Here are some examples:
- Healthcare: Hospitals and clinics face a high risk of medical malpractice lawsuits. These lawsuits can be very expensive to defend, and a successful claim can result in a significant financial loss. Healthcare providers need insurance policies that include coverage for medical malpractice.
- Construction: Construction companies face a high risk of worker injuries. These injuries can be caused by falls, heavy equipment, and other hazards. Construction companies need insurance policies that include coverage for workers’ compensation.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturers face a high risk of product liability lawsuits. These lawsuits can be filed if a product causes injury or damage. Manufacturers need insurance policies that include coverage for product liability.
- Technology: Technology companies face a high risk of cyberattacks. These attacks can result in data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage. Technology companies need insurance policies that include coverage for cyberattacks.
Coverage Options Available to Address Industry-Specific Risks
Commercial insurance policies offer a wide range of coverage options to address industry-specific risks. Here are some examples:
- Medical malpractice insurance: This type of insurance protects healthcare providers from financial losses resulting from medical malpractice lawsuits.
- Workers’ compensation insurance: This type of insurance protects employers from financial losses resulting from worker injuries.
- Product liability insurance: This type of insurance protects manufacturers from financial losses resulting from product liability lawsuits.
- Cybersecurity insurance: This type of insurance protects businesses from financial losses resulting from cyberattacks.
Emerging Trends in Commercial Insurance: What Is Commercial Insurance
The commercial insurance landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing risk profiles, and evolving customer expectations. These trends are shaping how insurance policies are designed, priced, and delivered.
Impact of Technology
Technological advancements are transforming the commercial insurance industry in several ways.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are being used to automate tasks, improve risk assessment, and personalize insurance offerings. Insurers are using these technologies to analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict potential risks. For example, AI-powered risk assessment tools can help insurers evaluate the safety of a manufacturing facility or the creditworthiness of a borrower.
- Internet of Things (IoT): The widespread adoption of connected devices is generating a wealth of data that can be used to improve risk management and pricing. For example, telematics devices in commercial vehicles can track driving behavior and provide insights into potential risks. This data can be used to offer discounts to safe drivers or to adjust premiums based on driving patterns.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology is being explored for its potential to streamline insurance processes and improve transparency. It can be used to create a secure and tamper-proof record of insurance transactions, which can help to reduce fraud and improve efficiency.
Data Analytics and Risk Management
Data analytics is playing an increasingly important role in risk management and insurance pricing. Insurers are using data to understand emerging risks, identify potential threats, and develop more accurate pricing models.
- Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics uses historical data to forecast future events. Insurers are using predictive models to estimate the likelihood of claims, assess the impact of natural disasters, and identify high-risk businesses.
- Data-Driven Risk Assessment: Insurers are using data to develop more sophisticated risk assessment tools. This allows them to tailor insurance policies to the specific needs of individual businesses and to offer more competitive pricing.
Evolving Risks and Policy Design
The changing global landscape is creating new risks for businesses.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Cyberattacks are becoming increasingly common, and businesses are facing significant financial losses due to data breaches and system failures. As a result, cybersecurity insurance is becoming increasingly important for businesses of all sizes.
- Climate Change Risks: The impacts of climate change, such as extreme weather events and rising sea levels, are posing new challenges for businesses. Insurers are developing new products and services to address these risks, such as flood insurance and climate change adaptation plans.
- Emerging Technologies: The rapid development of new technologies, such as artificial intelligence and autonomous vehicles, is creating new risks and opportunities. Insurers are working to understand the implications of these technologies and to develop new products and services to address them.
Resources and Further Information
Finding reliable information about commercial insurance is essential for businesses of all sizes. Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting, understanding the intricacies of commercial insurance can help you make informed decisions to protect your assets and minimize risks.
Industry Associations and Government Agencies
Industry associations and government agencies provide valuable resources and insights into commercial insurance. They offer guidance, research, and support for businesses navigating the insurance landscape.
- National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC): The NAIC is a non-profit organization that serves as a resource for state insurance regulators. They provide information on insurance regulations, consumer protection, and industry trends. [Link: https://www.naic.org/]
- Insurance Information Institute (III): The III is a non-profit organization that provides information and research on insurance issues. They offer educational materials, statistics, and resources for consumers and businesses. [Link: https://www.iii.org/]
- Small Business Administration (SBA): The SBA offers resources and support for small businesses, including information on commercial insurance. They provide guidance on choosing the right insurance coverage and accessing financing. [Link: https://www.sba.gov/]
Insurance Providers
Insurance providers are a primary source of information about commercial insurance. They offer a wide range of products and services, tailored to meet the specific needs of businesses.
- Large National Insurance Carriers: Companies like Liberty Mutual, Travelers, and Chubb offer a comprehensive range of commercial insurance products. They have extensive resources and expertise in various industries. [Link: https://www.libertymutual.com/, https://www.travelers.com/, https://www.chubb.com/]
- Regional and Local Insurance Brokers: Local brokers often have a deep understanding of the needs of businesses in their communities. They can provide personalized advice and guidance on insurance options. [Search for local insurance brokers in your area.]
- Online Insurance Marketplaces: Websites like Policygenius and Insureon offer online platforms to compare quotes from multiple insurance providers. This can save you time and effort in finding the best coverage. [Link: https://www.policygenius.com/, https://www.insureon.com/]
Books, Articles, and Online Platforms
In-depth learning about commercial insurance can be found in books, articles, and online platforms that offer comprehensive information and analysis.
- “The Business Owner’s Guide to Insurance” by Michael J. McLaughlin: This book provides a practical guide to understanding and managing insurance risks for small businesses. [Link: https://www.amazon.com/Business-Owners-Guide-Insurance-McLaughlin/dp/1599556785]
- “Commercial Insurance: A Practical Guide” by David M. Harbin: This book offers a detailed overview of commercial insurance concepts, types of coverage, and risk management strategies. [Link: https://www.amazon.com/Commercial-Insurance-Practical-David-Harbin/dp/0133368650]
- “The Insurance Journal”: This online publication provides news, analysis, and insights into the insurance industry, including commercial insurance trends and developments. [Link: https://www.insurancejournal.com/]
Commercial Insurance Blogs and Websites
Numerous blogs and websites offer insights, tips, and resources related to commercial insurance. These platforms provide valuable information on a wide range of topics, from risk management to industry-specific coverage.
- “The Hartford Business Blog”: This blog offers articles on insurance, risk management, and business topics relevant to commercial insurance. [Link: https://www.thehartford.com/business-blog]
- “The Insurance Insider”: This website provides news, analysis, and insights into the insurance industry, including commercial insurance trends and developments. [Link: https://www.insuranceinsider.com/]
Outcome Summary
Understanding commercial insurance is crucial for any business owner. By carefully assessing your risks, choosing the right coverage, and implementing sound risk management practices, you can ensure your business is protected from the unexpected, allowing you to focus on what matters most: growth and success.
Commercial insurance covers a wide range of risks for businesses, from property damage to liability claims. A key component of commercial insurance can be health insurance, which is crucial for protecting employees. If you’re looking for health insurance options in Ohio, you can explore health insurance ohio resources to find the right plan for your business.
Ultimately, commercial insurance helps businesses manage risk and protect their financial well-being.
